IEC Structural Forms for Electric Control panels and enclosures
Image Source: https://electrical-engineering-portal.com/
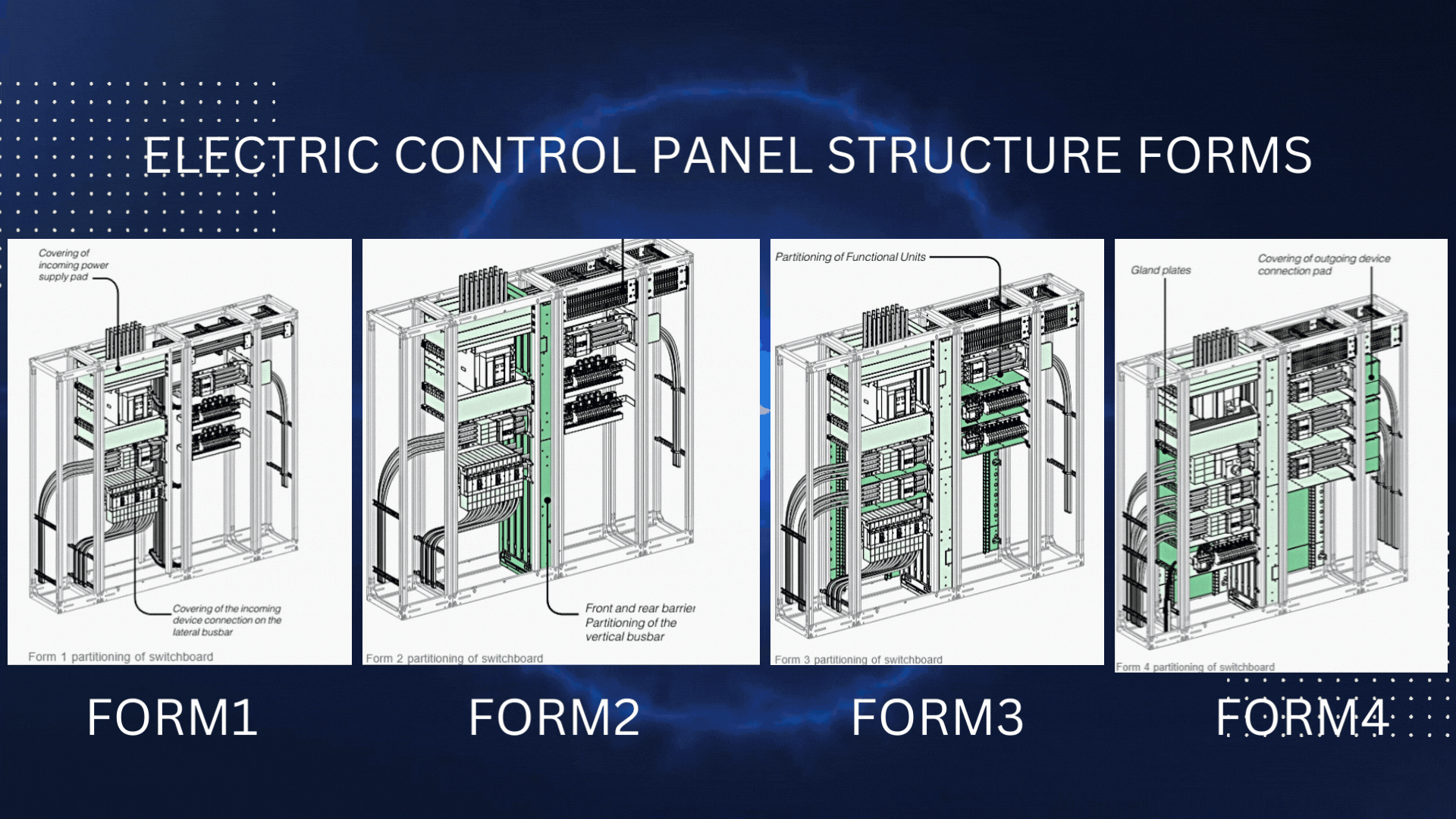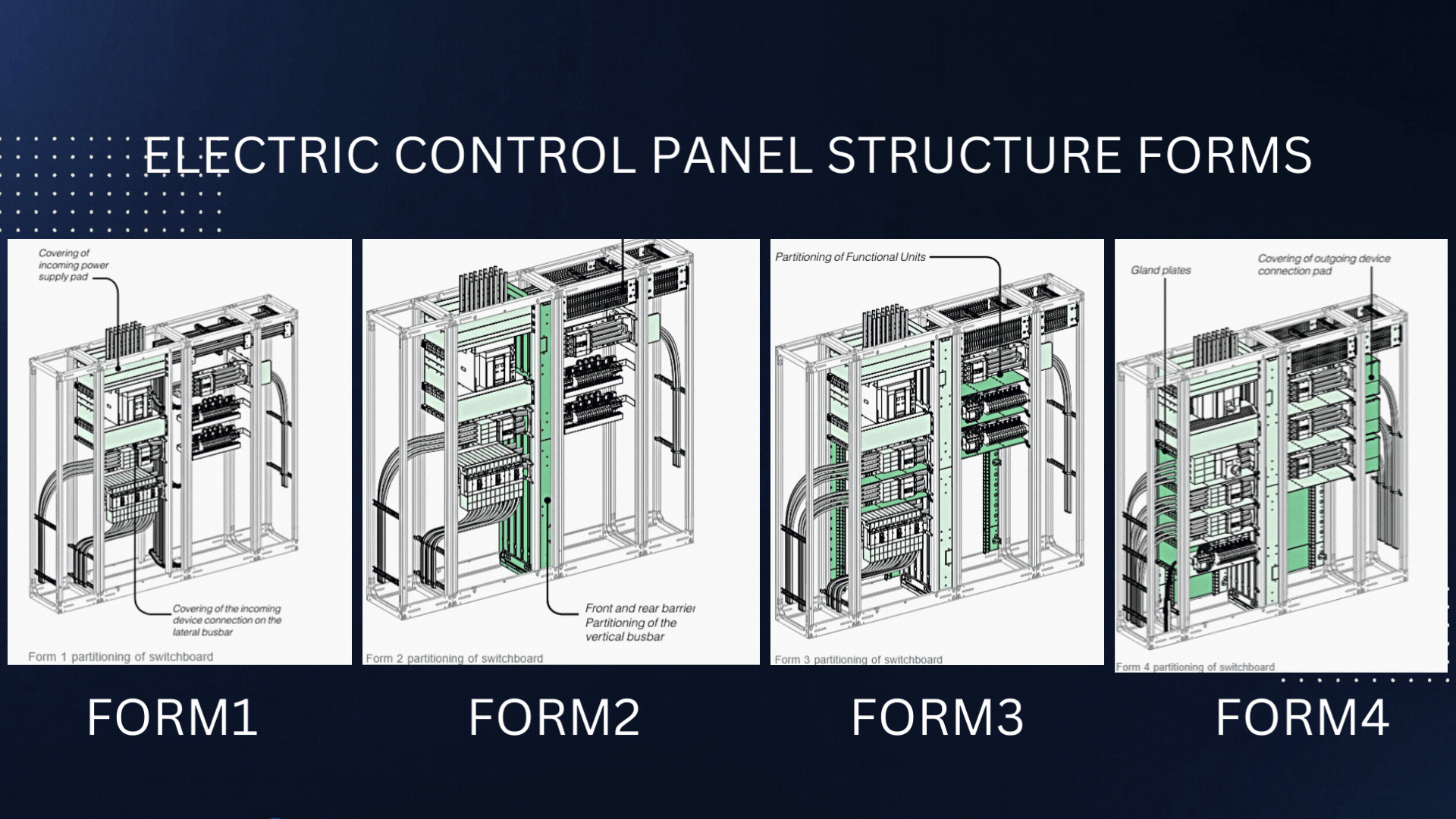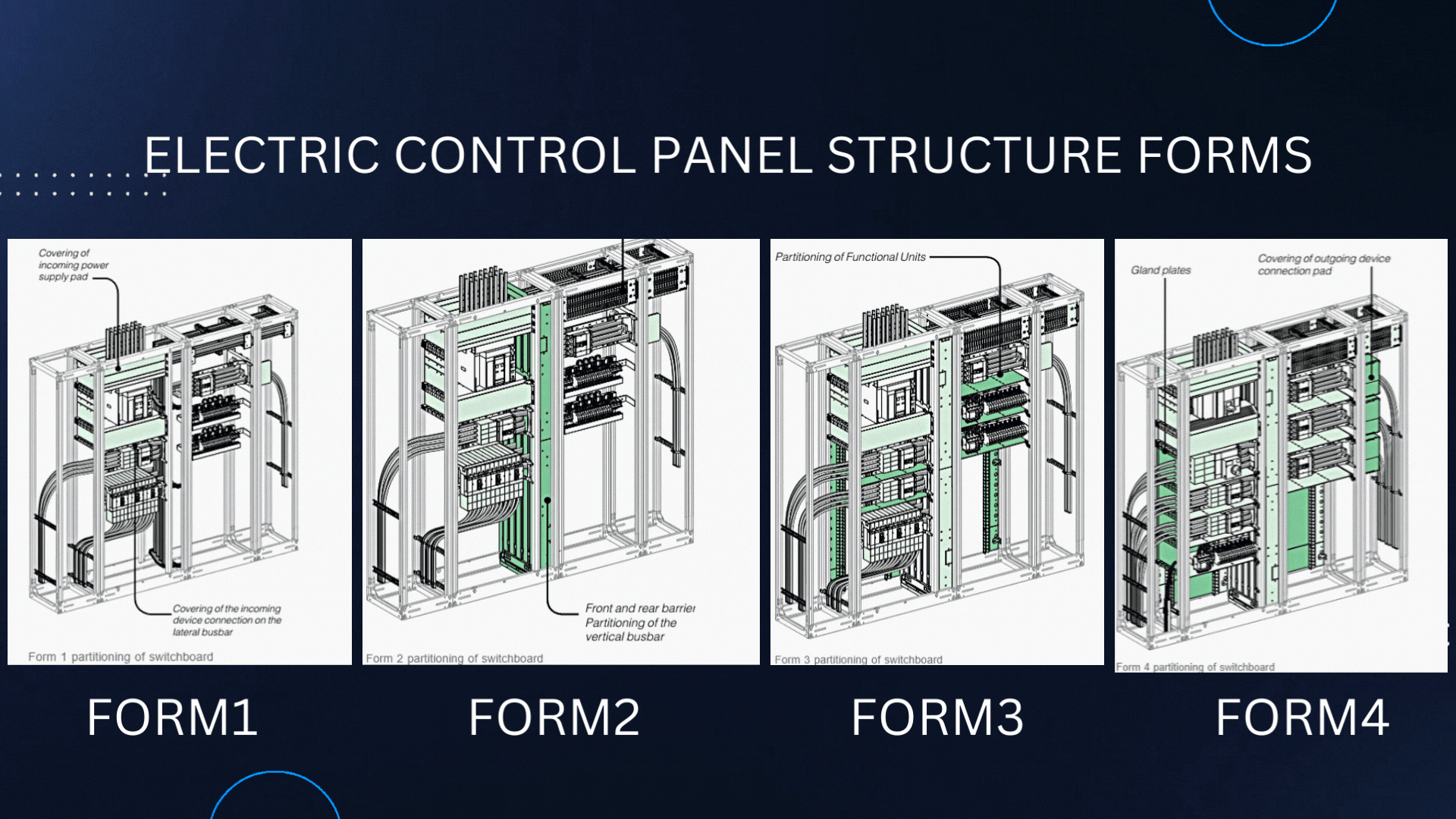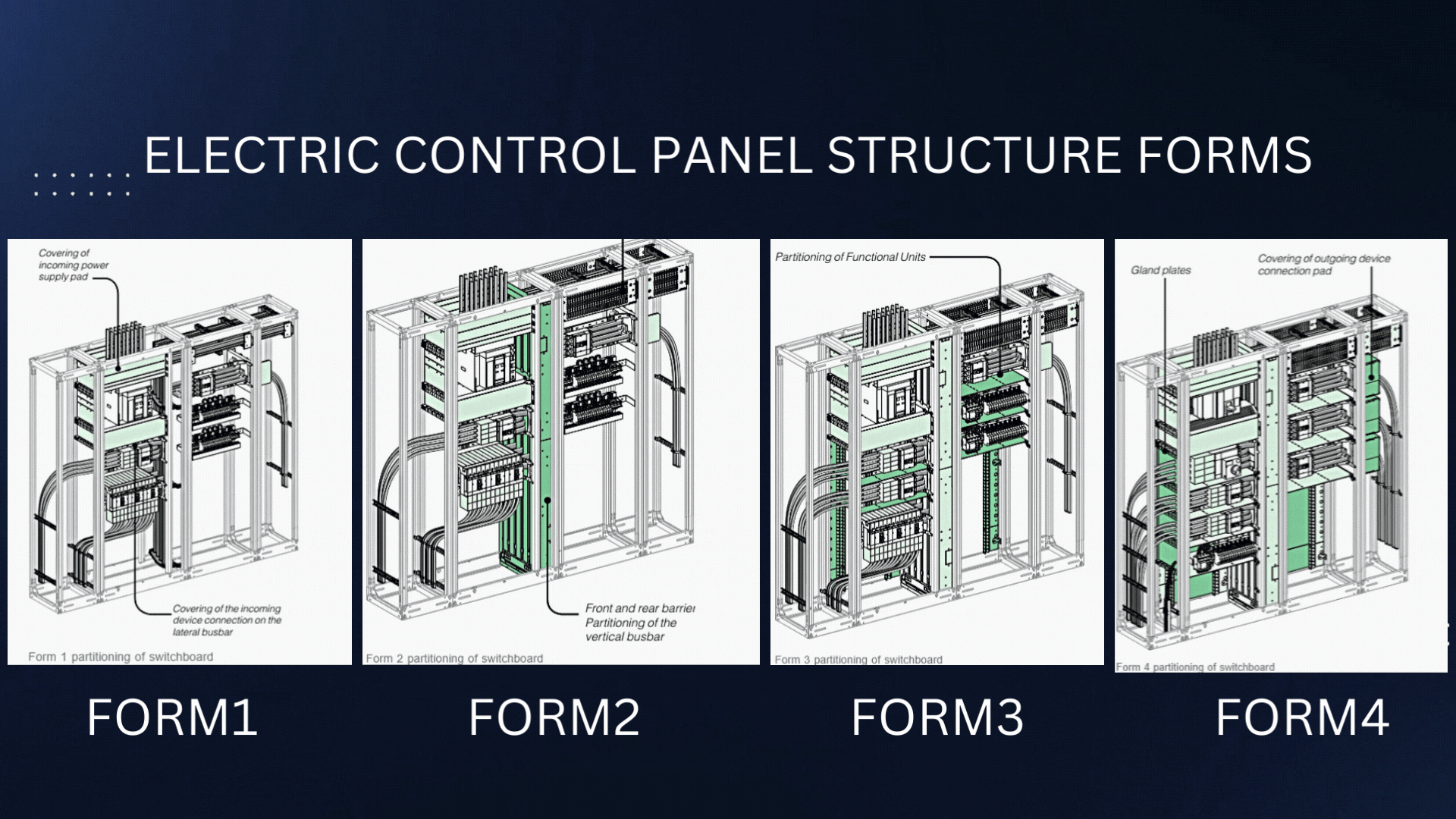
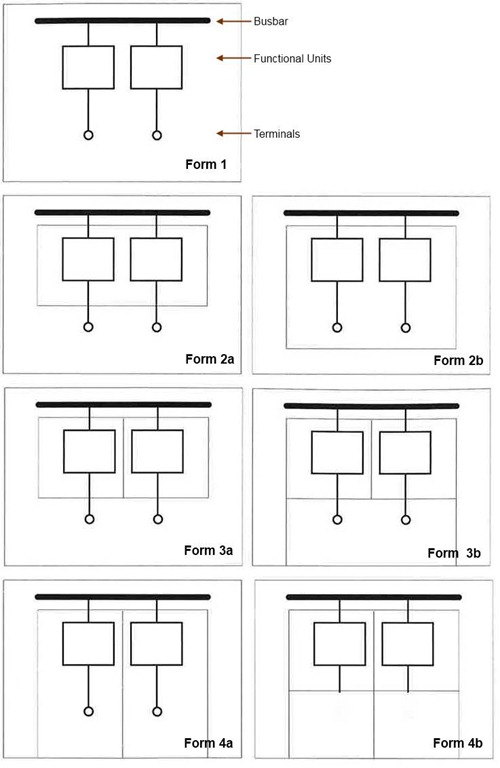
The structural forms of Electric Control panels are defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and are used to specify the type and degree of protection provided by an electrical enclosure. These forms provide guidelines for the design and construction of electrical enclosures used in low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies.
Form 1:
Form 1 enclosures are the most basic form of electrical enclosure and offer protection against accidental contact with live parts. They are typically used in applications where the electrical installation is in a dedicated room or area, and access to the enclosure is restricted. Form 1 enclosures are typically constructed of sheet metal and feature a simple, open design, with no barriers between the operator and the live parts.
Form 2:
Form 2 enclosures offer enhanced protection against accidental contact with live parts, with barriers or shields that prevent the operator from coming into contact with live parts, even if the enclosure door is open. They are typically used in applications where the electrical installation is located in a public area, or where access to the enclosure is not restricted. Form 2 enclosures are often constructed of sheet metal and may feature internal barriers or partitions to separate the live parts from the operator.
Form 3:
Form 3 enclosures offer protection against accidental contact with live parts and protection against the ingress of solid foreign objects. They are typically used in applications where the electrical installation is located in a dusty or dirty environment. Form 3 enclosures are often constructed of sheet metal and may feature internal barriers or partitions to separate the live parts from the operator. Additionally, they may include gaskets or seals to prevent dust or other foreign objects from entering the enclosure.
Form 4:
Form 4 enclosures provide the highest degree of protection against accidental contact with live parts and protection against the ingress of solid and liquid foreign objects. They are typically used in applications where the electrical installation is located in a harsh or hazardous environment, such as chemical plants or oil refineries. Form 4 enclosures are often constructed of sheet metal or other rugged materials and may include features such as gaskets, seals, and drains to prevent the ingress of liquids.
Form 4A and Form 4B are variations of the Form 4 structural form, which is the highest degree of protection against accidental contact with live parts and protection against the ingress of solid and liquid foreign objects. The main difference between Form 4A and Form 4B is the type of separation between the live parts and the operator, and the degree of protection against arc faults.
Form 4A:
Form 4A enclosures are similar to standard Form 4 enclosures in that they provide protection against accidental contact with live parts and the ingress of solid and liquid foreign objects. However, Form 4A enclosures have additional internal partitions or barriers that provide increased separation between the operator and the live parts. This increased separation helps to reduce the risk of arc faults and provides additional protection for the operator. Form 4A enclosures are typically used in applications where there is a higher risk of arc faults, such as in switchgear and controlgear assemblies.
Form 4B:
Form 4B enclosures provide the highest degree of protection against accidental contact with live parts and the ingress of solid and liquid foreign objects. They are similar to Form 4A enclosures in that they have additional internal partitions or barriers that provide increased separation between the operator and the live parts. However, Form 4B enclosures also have an additional degree of protection against arc faults, as they are designed to contain the energy from an arc fault within the enclosure. This helps to prevent injury to the operator and damage to the equipment. Form 4B enclosures are typically used in applications where there is a high risk of arc faults, such as in power distribution centers and switchgear rooms.
In summary, the different structural forms defined by the IEC provide guidelines for the design and construction of electrical enclosures with varying degrees of protection against accidental contact with live parts and the ingress of solid and liquid foreign objects. The choice of structural form will depend on the specific application requirements and the environment in which the electrical installation is located.
IEC standards related to panel structural forms and provides a brief description of each standard:
| IEC Standard Number | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IEC 60529 | Degrees of protection provided by enclosures (IP code) | This standard specifies the degree of protection provided by enclosures against the ingress of solid objects and liquids, as denoted by the IP code. The IP code is often used in conjunction with the panel structural forms to define the level of protection provided by the enclosure. |
| IEC 61439-1 | Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies – Part 1: General rules | This standard defines the general requirements for low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies, including requirements for the design and construction of enclosures. It references the panel structural forms defined in IEC 60529 to specify the degree of protection required for different types of enclosures. |
| IEC 62208 | Empty enclosures for low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies – General requirements | This standard specifies the general requirements for empty enclosures used in low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies, including requirements for the design and construction of enclosures. It references the panel structural forms defined in IEC 60529 to specify the degree of protection required for different types of enclosures. |
| IEC 61439-2 | Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies – Part 2: Power switchgear and controlgear assemblies | This standard specifies the requirements for power switchgear and controlgear assemblies, including requirements for the design and construction of enclosures. It references the panel structural forms defined in IEC 60529 to specify the degree of protection required for different types of enclosures. |
| IEC 61439-3 | Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies – Part 3: Distribution boards intended to be operated by ordinary persons (DBO) | This standard specifies the requirements for distribution boards intended to be operated by ordinary persons, including requirements for the design and construction of enclosures. It references the panel structural forms defined in IEC 60529 to specify the degree of protection required for different types of enclosures. |
| IEC 62271-200 | High-voltage switchgear and controlgear – Part 200: AC metal-enclosed switchgear and controlgear for rated voltages above 1 kV and up to and including 52 kV | This standard specifies the requirements for AC metal-enclosed switchgear and controlgear for rated voltages above 1 kV and up to and including 52 kV, including requirements for the design and construction of enclosures. It references the panel structural forms defined in IEC 60529 to specify the degree of protection required for different types of enclosures. |
Note that this is not an exhaustive list of all IEC standards related to panel structural forms, but rather a selection of some relevant standards.
IP ingress protection ratings as they relate to electric control panels per IEC 60529 standards:
| IP Code | Definition | Protection against solid objects | Protection against liquids |
|---|---|---|---|
| IP20 | Protection against solid objects larger than 12.5mm in diameter and not protected against water | Yes | No |
| IP30 | Protection against solid objects larger than 2.5mm in diameter and not protected against water | Yes | No |
| IP40 | Protection against solid objects larger than 1mm in diameter and not protected against water | Yes | No |
| IP41 | Protection against solid objects larger than 1mm in diameter and dripping water | Yes | Yes, vertically dripping water |
| IP42 | Protection against solid objects larger than 1mm in diameter and dripping water | Yes | Yes, dripping water at an angle of up to 15 degrees from vertical |
| IP43 | Protection against solid objects larger than 1mm in diameter and splashing water | Yes | Yes, water splashing from any angle up to 60 degrees from vertical |
| IP44 | Protection against solid objects larger than 1mm in diameter and splashing water | Yes | Yes, water splashing from any angle |
| IP54 | Protection against dust and splashing water | Yes | Yes, water splashing from any angle |
| IP55 | Protection against dust and water jets | Yes | Yes, water projected by a nozzle from any direction |
| IP56 | Protection against dust and powerful water jets | Yes | Yes, water projected in powerful jets from any direction |
| IP65 | Protection against dust and low-pressure water jets | Yes | Yes, water projected by a nozzle from any direction with limited ingress permitted |
| IP66 | Protection against dust and high-pressure water jets | Yes | Yes, water projected in powerful jets from any direction with limited ingress permitted |
| IP67 | Protection against dust and immersion up to 1 meter | Yes | Yes, immersion up to 1 meter |
| IP68 | Protection against dust and complete immersion | Yes | Yes, complete immersion for a specified period |
Note that while some of these IP ratings may be applicable to electric control panels, the IEC specifically defines the structural forms (Form 1, Form 2, Form 3, and Form 4) for these panels, which offer varying degrees of protection against contact with live parts and ingress of solid and liquid foreign objects.
